Network hardware
Network interface card (NIC)
A network interface card (NIC) is needed to allow a device to connect to a network (such as the internet).
It is usually part of the device hardware and contains the Media Access Control (MAC) address generated at the manufacturing stage.
Wireless network interface cards/controllers (WNICs) are the same as NICs in that they are used to connect devices to the internet or other networks.
However, they use wireless connectivity utilising an antenna to communicate with networks via microwaves.
They would normally plug into the USB port or be part of an internal integrated circuit.
Media Access Control (MAC)
A MAC address is made up of 48 bits which are shown as six groups of hexadecimal digits with the general format:
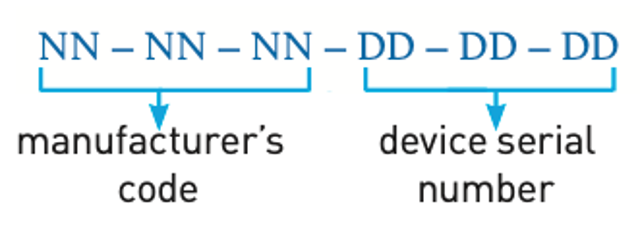
It should finally be pointed out that there are two types of MAC address:
- the Universally Administered MAC Address (UAA)
- the Locally Administered MAC Address (LAA).
The UAA is by far the most common type of MAC address and this is the one set by the manufacturer at the factory.
It is rare for a user to want to change this MAC address.
Internet protocol (IP) address
- When a device connects to a private network, a router assigns a private IP address to it.
- That IP address is unique on that network, but might be the same as an IP address on a separate network.
TIP
- IPv4 : 254.25.28.77
- IPv6 : A8FB:7A88:FFF0:0FFF:3D21:2085:66FB:F0FA
| MAC addresses | IP addresses |
|---|---|
| identifies the physical address of a device onthe network | identifies the global address on the internet |
| unique for device on the network | may not necessarily be unique |
| assigned by the manufacturer of the deviceand is part of the NIC | dynamic IP addresses are assigned by ISP using DHCP each time the device connects to the internet lsee later |
| they can be universal or local | dynamic IP addresses change every timea device connects to the internet; static IPaddresses don't change |
| when a packet of data is sent and received the MAC address is used to identify the sender's and recipients devices | used in routing operations as they specifically identify where the device is connected to the internet |
| use 48 bits | use either 32 bits (IPv4) or 128 bits IPv6 |
| can be UAA or LAA | can be static or dynamic |
static and dynamic IP address
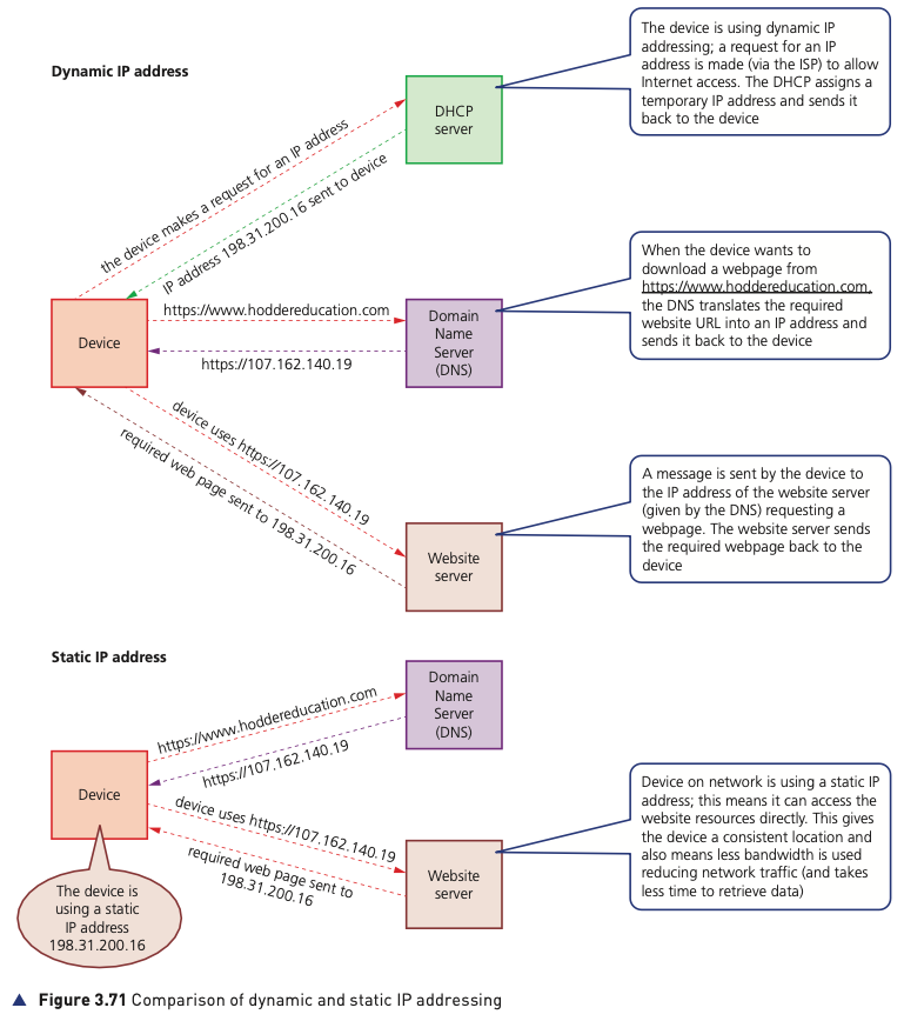
IP addresses can be either static (don’t change) or dynamic (change every time a device connects to the internet).
Static IP addresses are permanently assigned to a device by the internet service provider (ISP); they don’t change each time a device logs onto the internet.
Dynamic IP addresses are assigned by the ISP each time a device logs onto the internet. This is done using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
| Dynamic IP addresses | Static IP addresses |
|---|---|
| greater privacy since they change each timea user logs on | since static IP addresses don't change, theyallow each device to be fully traceable |
| dynamic IP addresses can be an issuewhen using, for example, VoIP since thistype of addressing is less reliable as itcan disconnect and change the IP address causing the VoIP connection to fail | allow for faster upload and download speeds |
| more expensive to maintain since the device must be constantly running so that information is always available |
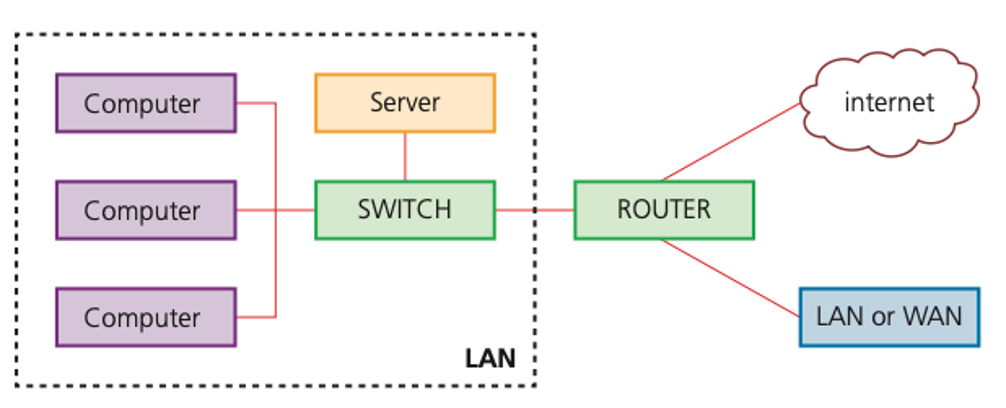
Routers
- Routers enable data packets to be routed between different networks, for example, to join a LAN to a WAN.
- The router takes data transmitted in one format from a network (which is using a particular protocol) and converts the data to a protocol and format understood by another network, thereby allowing them to communicate.